PCOD
Treatments
- Endometrial Receptivity Array
- Fertility Surgery
- IUI
- IVF
- Endocrinological Disease
- Fertility Booster Diet
- Weight Loss Management
Endometrial Receptivity Array
What is it?
 The term ERA stands for Endometrial Receptivity Analysis or Array. In this test, a small sample tissue from endometrial lining (innermost layer of Uterus) is used for evaluating whether the Uterus is ready for implantation of embryo or not.
The term ERA stands for Endometrial Receptivity Analysis or Array. In this test, a small sample tissue from endometrial lining (innermost layer of Uterus) is used for evaluating whether the Uterus is ready for implantation of embryo or not.
In the menstrual cycle of a woman the period from 19th to 23rd days is known as “implantation window” during which, the uterus gets prepared for the implantation process. It is part of the luteal phase and the endocrine part of ovaries is producing progesterone. This progesterone brings about modifications in the uterine wall so that, it gets prepared for receiving the embryo. The process involves formation of certain proteins that make the lining thicker and more receptive. In majority of females (84%) this window occurs at the exact time while in very few females (16%) this window occurs either before or after this period.
The IVF treatment in such cases fails as, the embryo transfer is occurring at wrong time. It is happening at the time, when the implantation window is either yet to open or has already been closed. So, the implantation is failing.
When is it prescribed?
It is prescribed in the patients where recurrent implantation failures are observed.
How is it done?
- A small endometrial tissue is collected and expression level of the gene 238 which determines endometrial receptivity is investigated.
- The technique involves assessing RNA levels in different stages of menstrual cycle. As this test is reproducible, its findings remain the same months after and hence, the test is not required to be repeated.
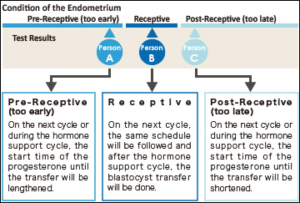
- This investigation can clearly indicate whether this implantation window of a particular woman is happening at the right time or the embryo transfer needs to be scheduled on the different date to match the window so that maturation of endometrial lining can be synchronized with embryo.
What are the advantages?
- Due to precise identification of Implantation Window, embryo transfer can be appropriately planned and can yield assured results.
- The agony of failed transfer can be got rid of.
- A minor shift by one of two days in embryo transfer can result into pregnancy.
Fertility Surgery
What is it?
A corrective surgery advised for the patients having structural abnormality of reproductive organs so as to improve the chances of conception. It can be for the male or the female partner.
How is it done?
First, minimal invasive diagnostic techniques are used to identify the problem and then a suitable surgical procedure is performed to correct it. The protocol can shortly shown as follows :
Female:
- Reversal of Tubectomy (Tubal ligation). The patient who has already undergone tubectomy for avoiding further pregnancies if decides to have a baby, this kind of surgery can be a solution wherein the ligatured (closed) fallopian tube is reconnected.
- Reconnecting fallopian tube: If there is blockage in fallopian tube due to some infection and pregnancy is not happening because of this, the tube can be reconnected surgically to solve the problem. It involves insertion of a small tube through cervix, uterus and connect the fallopian tube. The surgery is called Salpingostomy, sometimes called neosalpingostomy (the fallopian tube may be cut completely to open the passage for egg cells) or fimbrioplasty (when the tip of fallopian tube that is very close to ovarian is blocked, the tip if surgically opened).
- Polypectomy: A polyp is an abnormal collection of tissue. A polypectomy is a surgical procedure to remove polyps from the from an organ like Uterus. The procedure is relatively noninvasive and is usually carried out at the same time as a hysteroscopy.
- Myomectomy: This procedure sometimes also known as fibroidectomy, refers to surgical removal of uterinefibroids (leiomyomas). In comparison to hysterectomy, the uterus remains preserved in this procedure and the woman retains her reproductive potential.
- Dilatation for treating cervical stenosis: Cervical stenosis means a conditions wherein the cervix becomes extremely narrow. The treatment for this condition is using a dilator.
- Adhesiolysis: Some times, pelvic adhesions are observed blocking passage between uterus and ovarian. In such conditions natural pregnancy becomes difficult and even in ART oocyte pickup is obstructed by the adhesions. This disorder is treated by microsurgical technique or laparoscopic surgery to remove the adhesion and prevent its recurrence.
- Metroplasty: Sometimes, uterus is abnormal in shape such as ‘T’ or heart shaped and hence, can lead to complications during and after pregnancy. This condition is treated with metroplasty. The surgery involves reconstruction of uterine chamber to make into normal shape. With the surgery, implantation of embryo and further development is possible.
- PCO Drilling: Polycystic ovarian can cause the female body produce excess of testosterone and insulin, leading to fertility problems. High testosterone levels can cause irregular menstrual cycles, prevent ovulation and hinder pregnancy. Ovarian drilling can cure this problem Ovarian drilling is a laparoscopic procedure performed under general anesthesia. This surgery is typically done on an outpatient basis with minimal recovery time. With a laparoscopic tool small openings are mad in ovarian.
- Ovarian cystectomy: Endometriomas or chocolate cysts are benign masses growing around ovarian and obliterate the normal process of ovulation. Removal of these cysts is called cystectomy. The surgery needs to be done very carefully as there is a possibility of damage to ovarian vascular supply. Further, there is some decline in ovarian functioning after surgery. So, ART may be necessary for pregnancy.
Male:
- Treat varicocele(swelling of veins coming of Testis) which will allow testes to produce better sperms.
- Removal of blockage in the Epididymis (tubular extension of testis responsible for activation of spermatozoa).
- Reversal of Vasectomy. This is done when the couple decides to go for pregnancy after vasectomy surgery.
- Removal of sperms from testis surgically in case of Azoospermia (Absence of sperms in Ejaculate).
IUI: Intra Uterine Insemination
What is it?
It literally means artificial release of sperms directly into uterine cavity by bypassing the cervix and vagina. A doctor releases sperms into the woman’s uterus (Womb). These sperms then move towards fallopian ducts (ovarian ducts) where they can unite with egg cells to gradually develop into embryo (Foetus). The efforts involved in sperms’ movement from vagina to fallopian duct are avoided. Usually, the extremely narrow passage of cervix limits number of sperms passing through it into uterus. The IUI technique minimizes sperms’ efforts for swimming upto fallopian tube.
When is it necessary?
The doctor recommends this technique when pregnancy does not result even after repeated attempts and one of the following is the reason for this.
Infertility factors in males
- Oligospermea: Sperm count in the semen of male partner is remarkably low.
- Asthanospermea: The sperm count may be adequate or inadequate but their motility is very low.
- Teratospermea: The sperms are morphologically abnormal. The male partner is not able to have proper erection or undergoes retrograde ejaculation and hence, is not able to release semen into vagina.
- Hypospadias / Hyperspadiasis: The urethral opening is not located properly.
Infertility factors in females
- Obstructive mucous: Mucous in the cervix of the female partner is scanty, thick and sticky which obstructs the passage of sperms through it.
- Scarred cervix: Due to earlier procedures Cervix has scars that hinder the movement of sperms.
Advantages of IUI:
- In above mentioned conditions IUI can lead to fertilization and subsequently pregnancy.
- As most healthy sperms are separated and used in the procedure, the chance of conceiving are better.
- It is minimal invasive procedure and hence less painful.
- It is considerably cost effective as compared to other IVF procedures.
When it is not recommended?
IUI is not prescribed when any one or more of the following conditions is diagnosed.
- If the female partner has blocked fallopian tubes for some reason.
- If she has some serious pelvic infection.
- If she is diagnosed with endometriosis.
IVF : In Vitro Fertilization
What is it?
During IVF, an egg is removed from the woman’s ovaries and fertilised with sperm in a laboratory. The fertilised egg, called an embryo, is then returned to the woman’s womb to grow and develop. It can be carried out using patient’s eggs and partner’s sperm, or eggs and/or sperm from donors.
When is it recommended?
Offered to women under the age of 43 who have been trying to get pregnant through regular unprotected sex for 2 years, or who have had failed cycles of artificial insemination.
How is it done?
IVF involves 6 main stages:
1. suppressing your natural cycle– the menstrual cycle is suppressed with medication
2. boosting your egg supply– medication is used to encourage the ovaries to produce more eggs than usual
3. monitoring your progress and maturing your eggs– an ultrasound scan is carried out to check the development of the eggs, and medication is used to help them mature
4. collecting the eggs– a needle is inserted into the ovaries, via the vagina, to remove the eggs
5. fertilizing the eggs– the eggs are mixed with the sperm for a few days to allow them to be fertilised
6. transferring the embryo(s)– 1 or 2 fertilised eggs (embryos) are placed into the womb
Once the embryo(s) has been transferred into patient’s womb, she’ll need to wait 2 weeks before taking a pregnancy test to see if the treatment has worked.
Endocrine diseases
What is it?
Endocrine glands in the body are responsible for secretion of hormones which are carried through blood and regulate functioning of different body systems. Fluctuations in levels of these hormones can lead to physiological disorders.
What are they?
- Thyroid hormones: Thyroid gland situated near larynx secretes Tri-iodothyronine (T3) and Tetra-iodothyronine (T4) which regulate general body metabolism. Though not directly, the gland also affects secretion of gonadal hormones.
- Pituitary hormones: Pituitary gland is generally described as master endocrine as it regulates functioning of other endocrine glands. It secretes following hormones.
- Prolactin: This hormone is primarily responsible for triggering secretion of milk by mammary glands. In addition, it has a significant role in regulating menstrual cycle and ovulation.
- Follicle Stimulating Hormone: It is directly responsible for maintaining regularity of menstrual cycle. It in fact, stimulates development and maturation of ovarian follicles and thus, ovulation process. Fluctuation in levels of this hormone can disturb ovulation process.
- Luteinizing hormone: Actual release of matured oocyte (Egg cell) from the ovarian is triggered by this hormone. It is this oocyte that has to be fertilized for development into embryo. Test for ovulation involve testing level of this hormone.
- Progesterone: This hormone is secreted by Corpus Luteum in the ovarian and is responsible for thickening of endometrial wall (innermost covering of uterus) that is required for implantation and development of embryo. Reduced levels of this hormone can cause miscarriage.
- Anti-Mullerian Hormone: Ovarian follicles secrete this hormone and it supports the immature egg cell. Levels of this hormone in blood can indicate the number of eggs in ovarian.
How are they significant in fertilitiy?
Hormone imbalance can lead to various issues that may affect the fertility and cause issues as follows:
- Ovulatory dysfunction: Thyroid and pituitary disorders and lead to abnormalities in ovulation process. Polycystic ovarian can also affect the ovulation. Irregularities in ovulation are likely to affect fertility of the female.
- Disorders of Luteal phase: After release of mature oocyte from ovarian, there is formation of Corpus Leuteum from remains of the follicle. It secretes progesterone essential for thickening of endometrium. Normally, this process (Luteal Phase) goes on for 14 days. If this phase is shorter than 10 days, implantation of embryo can not happen thus resulting into absence of pregnancy.
How is it diagnosed?
Following conditions indicate possibility of hormonal imbalance.
- Irregularity in menstrual cycle.
- Spotting or white discharge.
- Appearance of acne.
- Male pattern body hair development.
- Weight gain for no significant reason.
- Unexplained extreme mood changes.
Fertility Booster Diet
Intake of proper food becomes very important during the fertility treatment. Eating certain foods during different phases of your menstrual cycle can enhance the fertility. So, if a woman wants to maximize her chances of conceiving, it is possible to eat foods that have advantageous to each phase. So, we ask our experts to weigh in on what to actually eat during each of the reproductive phase.
The list includes:
1. Plenty of fruits and vegetables
2. Complex carbohydrates – whole grains like brown rice , oats and whole meal bread .
3. Organic food where possible.
4. Oily foods like nuts, fish and oil.
5. Add lemon , pomegranate, green leafy vegetables and tomatoes to diet .
6. Flax seeds + sunflower seeds .
7. Avoid trans fats.
8. Increase intake of fibre.
9. More fish and organic eggs than red meat .
10. Avoid additive ,preservatives and artificial sweetner.
11. Reduce and avoid sugar both on its own and hidden in food .
12. Avoid caffeine : coffee, chocolate ,tea ,cola & alcohol .
13. Avoid processed food.
14. Try having fresh and home-made food.
Weight Loss Management
What is it?
It is avoiding weight gain or losing weight for improving the chances of conceiving. Too low or too high body weight can interfere with fertility of an individual and hence, needs to be managed appropriately.
How is it done?
Normally, weight loss management involved diet and exercise. The couple trying for pregnancy needs to take careful measures in this. Proper diet and moderate exercise are best recommended for weight loss. But during pregnancy if necessary, weight management must be done preferably by diet control. Heavy exercise can affect the embryonic development in uterus and hence, has to be avoided.
When is it recommended?
Excess body weight in female partner is known to reduce the possibility or pregnancy. There is a need to manage the weight appropriately for natural pregnancy or even IVF. When an obese patient approaches for IVF treatment, before treatment the patient needs to undergo weight management regime and only then the IVF protocol can be followed. As mentioned above, the weight loss should be by controlled diet and not entirely by exercise.
